Radial Forging Machines
Radial Forging Technology as a central forming unit in the steelworks
Steel and Special Alloys industry
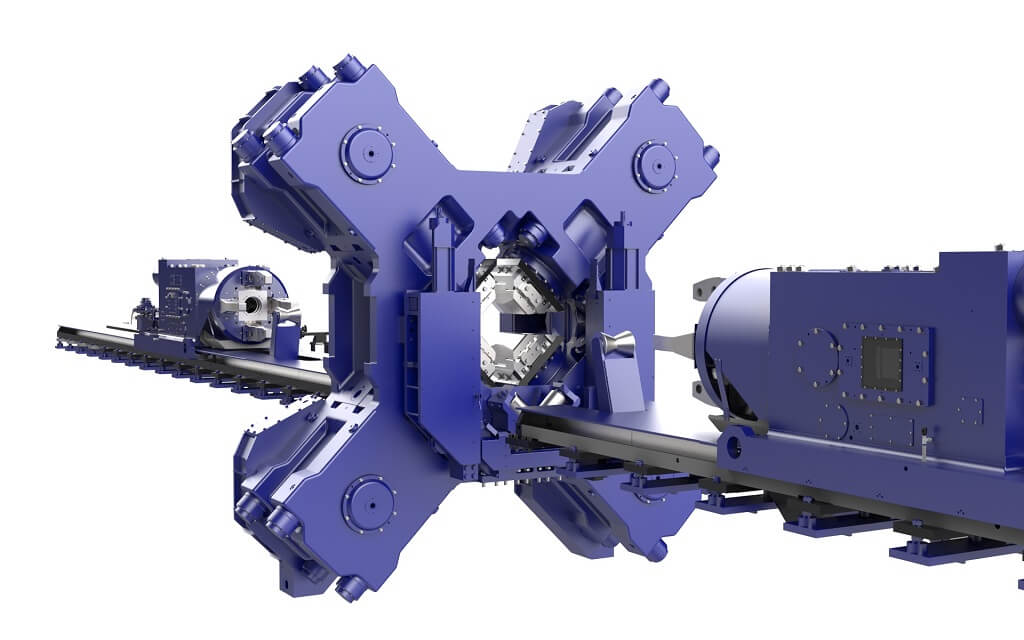
Our radial forging machines have become firmly established in the forming of cast, continuous cast, ingots and remelts to bars as well as to stepped shafts or axles. They have been used successfully for any steel grade, super alloys, titanium and many other metals for many decades. The outstanding forming properties and dimensional accuracies, combined with high productivity, are unique among the forging systems.
Technology
Forming requirements
For quick and cost-efficient forming
The cast structure is to be converted into a forged structure to achieve the required mechanical values. Degree of porosity, gran size and carbide distribution are features of interest for the semi-finished products. The overall forming is done in incremental steps. The capability to process from all sides permits high degrees of forming in one heat and thus quick and cost-efficient forming.
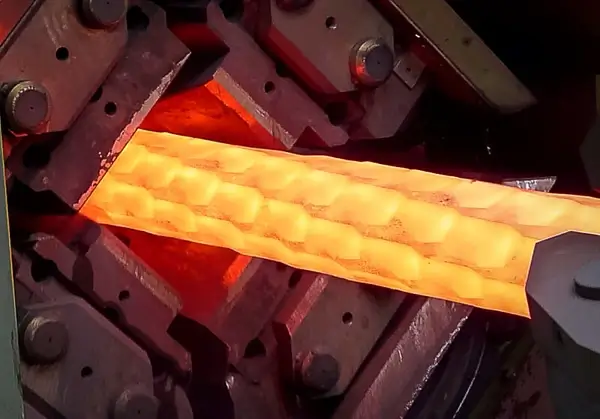
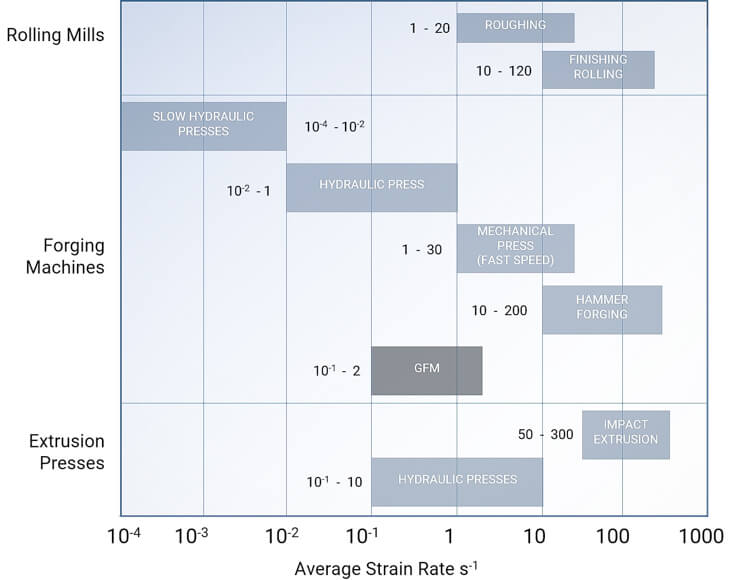
Forming characteristics
Our forging machines can be characterized as stroke- and power-limited forming machines. The forming energy is stored in flywheels. From a metallurgy point of view, our machines are quick-running presses, rather than “forging hammers”.
Your advantages
- High throughput / sustainable process
- Best metallurgy values
- Large dimensional rangeof one-heat process
- Efficient forming of parts with inner and/or outer shapes
- High accuracy
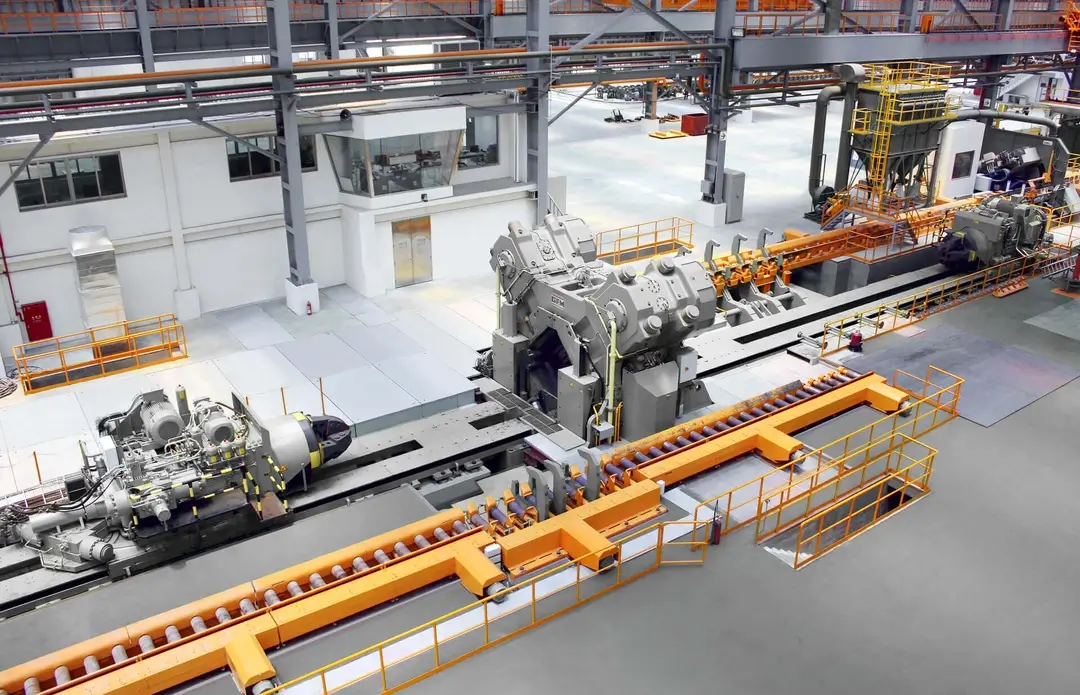
Machine types
A selection from our machine range.
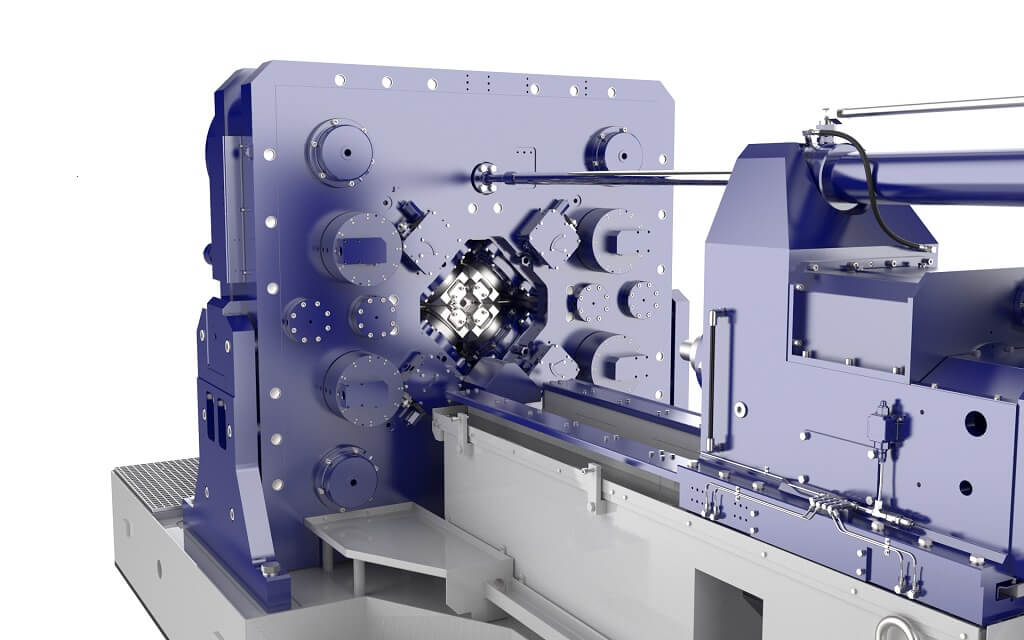
Products and markets
Where to find GFM machines.
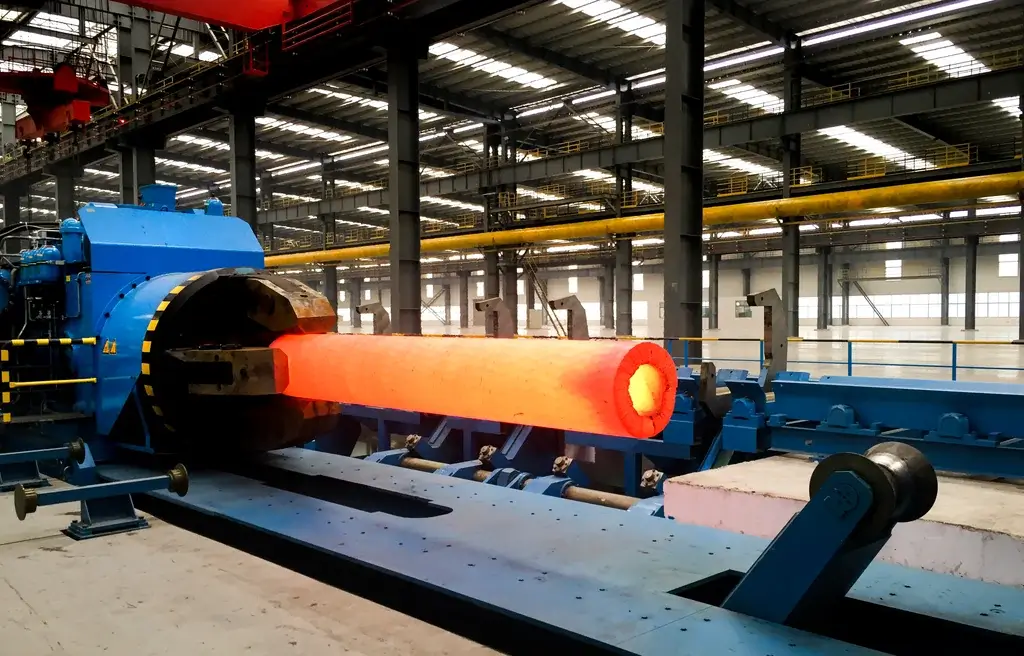
The combination of good core penetration (compared to rolling) and high throughput while maintaining an excellent temperature control (compared to open-die presses) permits highly efficient forming.
Your advantages
- Excellent surface and straightness
- Even mechanical properties
- High output and high throughput
- Products with lengths exceeding 30 m
- High degree of automation
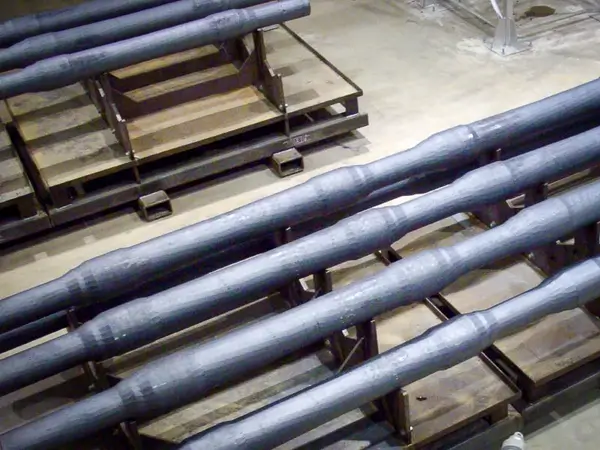


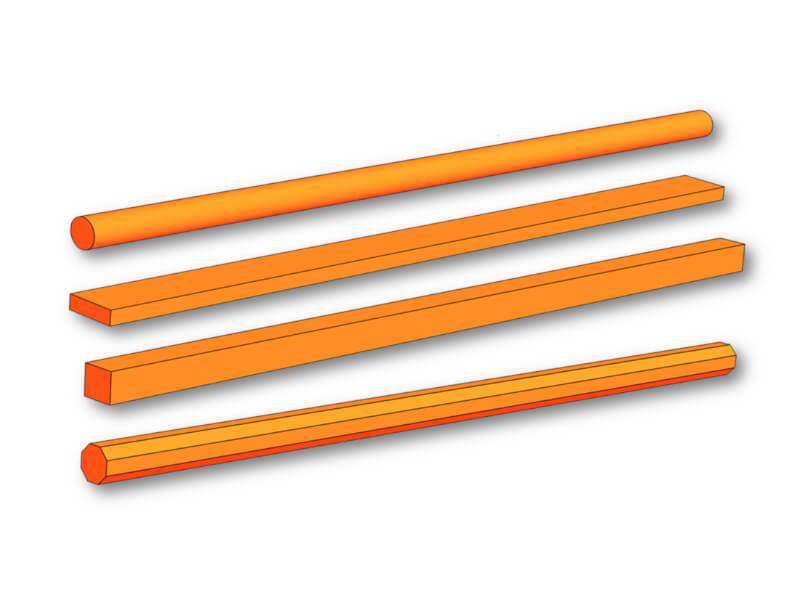
Bars
Round, square, rectangular, octagonal
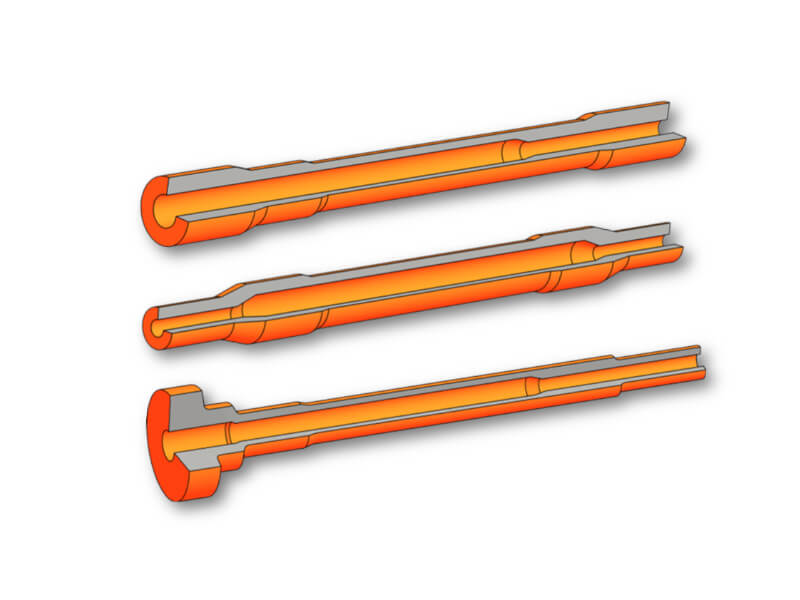

Shafts
Inner and outer steps or contours
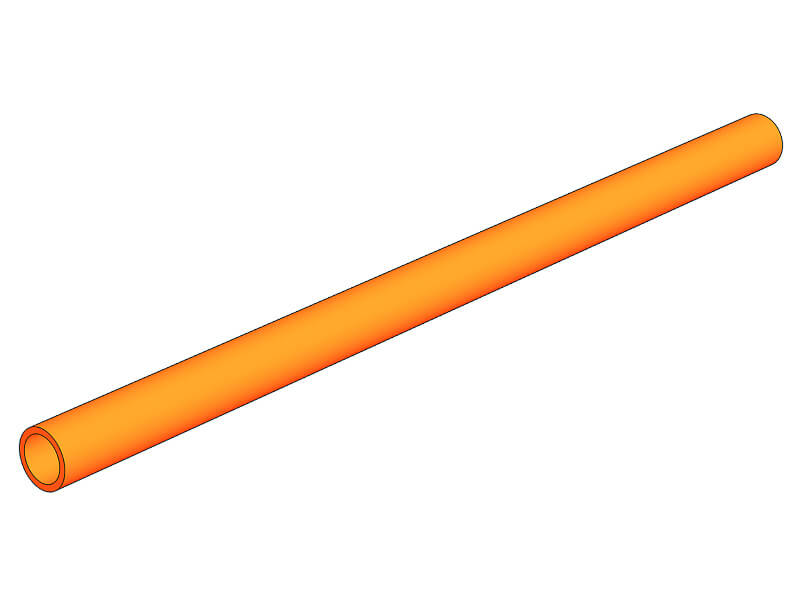
Pipes
Cylindrical or conical
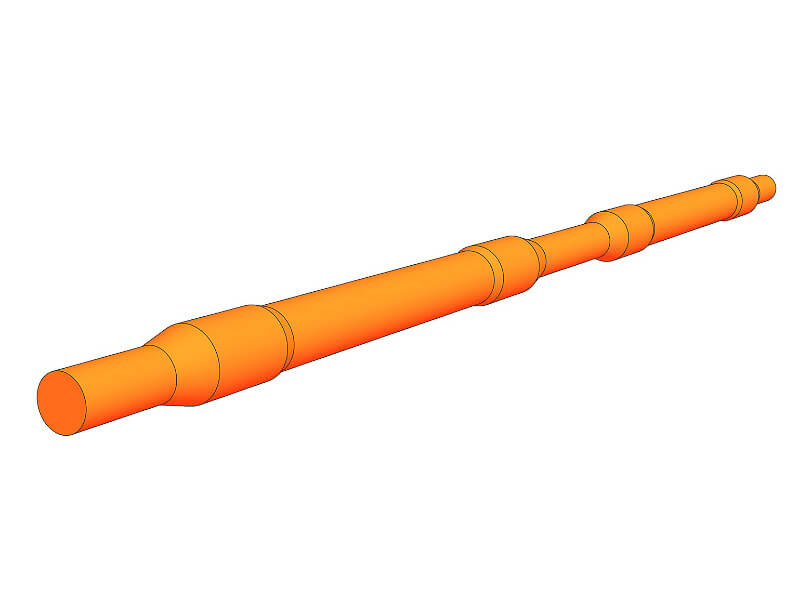
Stepped parts
Shafts, axles, flanges
